-

 Every day in the U.S., 9 people are killed and more than 1,060 people are injured in crashes that are reported to involve a distracted driver. The cause for concern is obvious. Transportation related occupational fatalities are the number one cause of death in the American workforce. The purpose of this lesson is to heighten drivers’ awareness of the dangers of distracted driving and identify ways to stay safe when sharing the road with distracted drivers.
Every day in the U.S., 9 people are killed and more than 1,060 people are injured in crashes that are reported to involve a distracted driver. The cause for concern is obvious. Transportation related occupational fatalities are the number one cause of death in the American workforce. The purpose of this lesson is to heighten drivers’ awareness of the dangers of distracted driving and identify ways to stay safe when sharing the road with distracted drivers. -

 DOT Hazardous Materials General Awareness consists of five lessons, The goal of this library is to offer the required DOT awareness-level lessons that help save lives in high risk work environments, particularly those that involve transporting hazardous materials. The first lesson is DOT Fundamentals of Hazardous Materials. This lesson provides an overview of the hazardous materials transport process and introduces the learner to the many references used during that process.
DOT Hazardous Materials General Awareness consists of five lessons, The goal of this library is to offer the required DOT awareness-level lessons that help save lives in high risk work environments, particularly those that involve transporting hazardous materials. The first lesson is DOT Fundamentals of Hazardous Materials. This lesson provides an overview of the hazardous materials transport process and introduces the learner to the many references used during that process. -

 When on the road, job, and everywhere in-between, identifying hazardous materials and knowing exactly how to handle them is one of the most important tasks a worker must know. Because of the importance of identifying these hazardous materials properly, the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) requires all workers that handle these materials to take safety training in order to help protect themselves as well as others around them.
When on the road, job, and everywhere in-between, identifying hazardous materials and knowing exactly how to handle them is one of the most important tasks a worker must know. Because of the importance of identifying these hazardous materials properly, the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) requires all workers that handle these materials to take safety training in order to help protect themselves as well as others around them. -

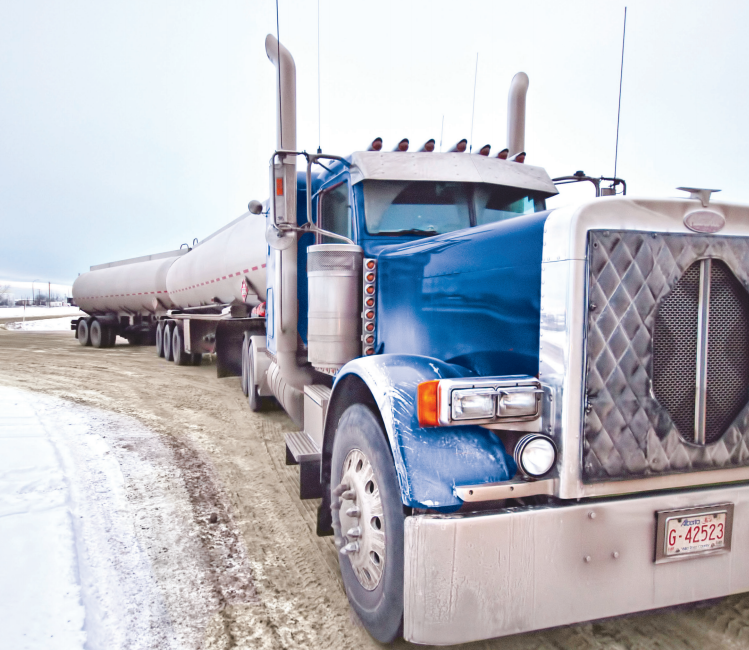
 DOT Packaging Hazardous Materials is part of our DOT Transportation library. It covers the steps for packaging a hazardous material, how to select appropriate hazardous materials packaging and how to determine and prepare required hazardous materials identifiers, including labels, markings, placards, and shipping papers.
DOT Packaging Hazardous Materials is part of our DOT Transportation library. It covers the steps for packaging a hazardous material, how to select appropriate hazardous materials packaging and how to determine and prepare required hazardous materials identifiers, including labels, markings, placards, and shipping papers. -

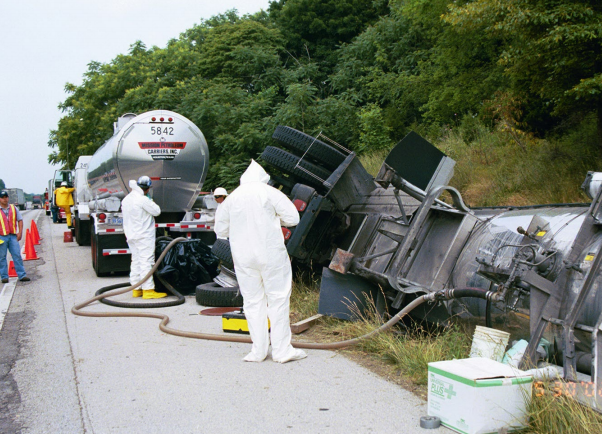
 Emergency planning is critical for operations that handle or produce significant quantities of hazardous materials. Because of the danger to employees working at these facilities and to the general public presented by the harmful release of hazardous materials, likes noxious, combustible gases and waste, people have a right to know about the potential for danger involved in related operations.
Emergency planning is critical for operations that handle or produce significant quantities of hazardous materials. Because of the danger to employees working at these facilities and to the general public presented by the harmful release of hazardous materials, likes noxious, combustible gases and waste, people have a right to know about the potential for danger involved in related operations. -
 In this course you will learn how to identify how noise impacts hearing and the factors that determine the extent of hearing loss, identify noise exposure levels that require hearing protection according to Part VII of Canadian Regulations, identify how the types of hearing protectors are selected for a job, and their advantages and disadvantages for controlling noise exposure, identify correct use, care, and maintenance practices for hearing protectors and identify the requirements of a Hearing Conservation Program.
In this course you will learn how to identify how noise impacts hearing and the factors that determine the extent of hearing loss, identify noise exposure levels that require hearing protection according to Part VII of Canadian Regulations, identify how the types of hearing protectors are selected for a job, and their advantages and disadvantages for controlling noise exposure, identify correct use, care, and maintenance practices for hearing protectors and identify the requirements of a Hearing Conservation Program.